Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) have long been recognized as the gold standard for testing the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical interventions. Despite their rigorous methodology, RCTs are not without limitations – logistical demands, recruitment hurdles, elevated costs, selection bias, inability to detect rare and long-term adverse effects, and limited generalizability to everyday clinical settings. Many patients, federal legislation, and regulatory agencies, and biopharmaceutical companies are hopeful that Real-World Data (RWD) could supplement RCTs, provided its quality is good enough.
In 2016, an expert panel delineated three core dimensions – conformance, completeness, and plausibility to evaluate the intrinsic data quality of Electronic Health Record (EHR) databases [1]. This multi-dimensional framework has catalyzed a series of academic endeavors and industry initiatives aimed at refining the methodologies for RWD quality assessment and enhancement [2-7] and to implement model-driven, quantitative approaches to address RWD completeness and plausibility issues [8-11].
Despite the proliferation of top-down strategies to assess RWD quality, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advocates for a nuanced, fit-for-purpose approach that necessitates individualized, bottom-up assessments. This recommendation aligns with our endeavor to apply a granular quality evaluation framework to a specific real-world application: the assessment of time to treatment discontinuation (rwTTD) in the context of systemic anticancer therapies [12].
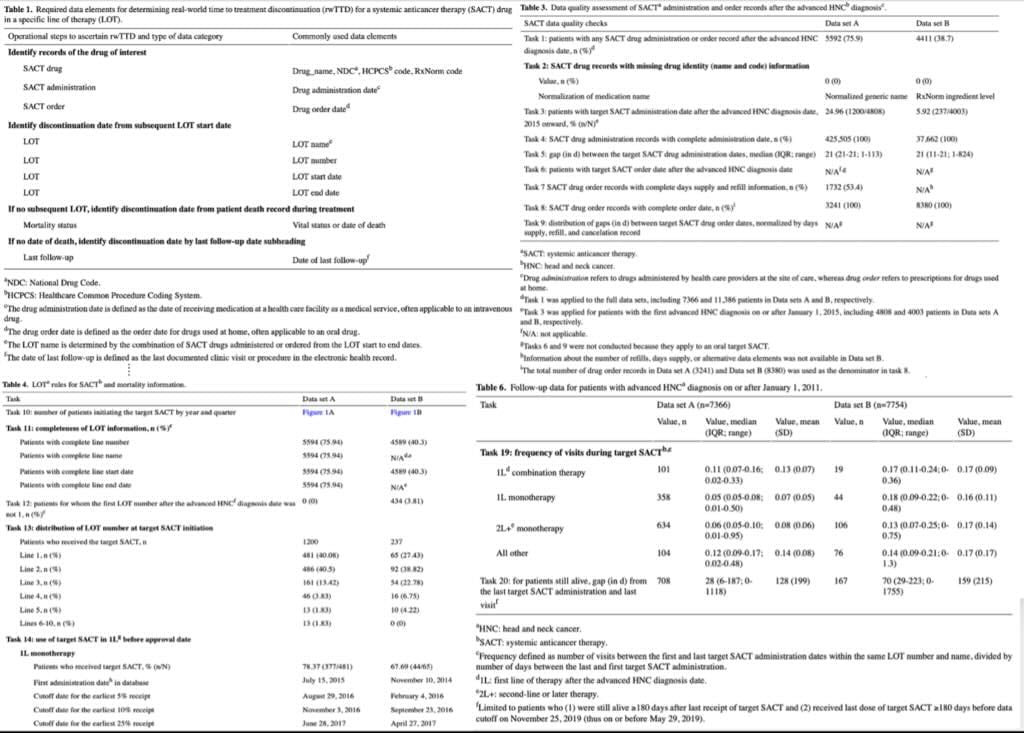
Our case study [12] focuses on an operational definition of rwTTD within oncology and gauges the data completeness and plausibility related to anticancer treatment regimens. Through a meticulous examination of 20 distinct tasks encompassing Line of Therapy (LoT), death date, and length of follow-up, we embarked on a detailed scrutiny of two prevailing EHR databases, with the objective of estimating rwTTD for a specific anticancer agent in advanced head and neck carcinoma.
The comparative analysis of these databases unveiled disparities in drug nomenclature, treatment sequencing, and mortality data completeness, shedding light on the inherent variability in RWD sources and underscoring the imperative for rigorous, context-specific quality assessments (see Figure 1).
In sharing our findings and methodological advancements, our goal is to cultivate a culture of collaboration among researchers, galvanizing a united effort to enhance the quality of Real-World Data (RWD), thereby augmenting its value in clinical research. We champion ongoing discourse and the exchange of knowledge within the scientific community, aiming to accelerate the assimilation of RWD as a formidable complement to conventional clinical trial frameworks. If this vision resonates with you, we warmly invite you to join us in this endeavor.
References:
1. Kahn MG, Callahan TJ, Barnard J, Bauck AE, Brown J, Davidson BN, et al. A harmonized data quality assessment terminology and framework for the secondary use of electronic health record data. EGEMS (Wash DC). 2016;4(1):1244.
2. Mahendraratnam N, Silcox C, Mercon K, Kroetsch A, Romine M, Harrison N, et al. Determining real-world data’s fitness for use and the role of reliability: Duke-Margolis Center for Health Policy. Duke Margolis Center for Health Policy. 2019. URL: https://healthpolicy.duke.edu/publications/determining-real-world-datas-fitness-use-and-role-reliability
3. Callahan TJ, Bauck AE, Bertoch D, Brown J, Khare R, Ryan PB, et al. A comparison of data quality assessment checks in six data sharing networks. EGEMS (Wash DC). Jun 12, 2017;5(1):8.
4. Reynolds MW, Bourke A, Dreyer NA. Considerations when evaluating real-world data quality in the context of fitness for purpose. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. Oct 2020;29(10):1316-1318.
5. OHDSI: data quality dashboard. GitHub. URL: https://github.com/OHDSI/DataQualityDashboard
6. PEDSnet/data quality analysis. GitHub. URL: https://github.com/PEDSnet/Data-Quality-Analysis/blob/master/Data/DQACatalog/DQA_Check_Type_Inventory.csv
7. DQUEEN v 0.5 (data QUality assEssmENt and managing tool). GitHub. URL: https://github.com/ABMI/DQUEEN_OMOP_CDM_Version
8. Estiri H, Klann JG, Murphy SN. A clustering approach for detecting implausible observation values in electronic health records data. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. Jul 23, 2019;19(1):142.
9. Estiri H, Murphy SN. Semi-supervised encoding for outlier detection in clinical observation data. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. Nov 2019;181:104830.
10. Estiri H, Klann JG, Weiler SR, Alema-Mensah E, Joseph Applegate R, Lozinski G, et al. A federated EHR network data completeness tracking system. J Am Med Inform Assoc. Jul 01, 2019;26(7):637-645.
11. Huser V. Facilitating analysis of measurements data though stricter model conventions: exploring units variability across sites. Observational Health Data Sciences and Informatics. 2017. URL: https://www.ohdsi.org/web/wiki/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=resources:huser-2017-ohdsi-symp-units.pdf
12. Ru B, Sillah A, Desai K, Chandwani S, Yao L, Kothari S. Real-World Data Quality Framework for Oncology Time to Treatment Discontinuation Use Case: Implementation and Evaluation Study. JMIR Med Inform 2024;12:e47744